ASTM D2000 Specifications for Rubber Materials
ASTM D 2000 – Standard Classification System for Rubber Products in Automotive Applications
This standard outlines the system used to classify the properties of vulcanized rubber materials, which are, ideally used, for automotive applications. The classification system helps to determine properties of vulcanized rubber materials associated with 1) the type identified by heat aging resistance 2) the class identified by resistance to swelling in oils.The purpose of this classification system is to provide guidance to the engineer in the selection of practical, commercially available rubber materials, and further to provide a method for specifying these materials by the use of a simple “line call-out” designation.
An ASTM D2000 “line call-out” does not specify the ingredients of an elastomer compound. It dictates the physical property requirements, e.g. hardness, tensile strength, elongation at break, heat resistance, oil resistance etc., that the compound formulation must meet. Basically speaking, it is a way to define the material properties required, in a standardized format, to meet the anticipated service environment and to insure consistent material quality in production. It is much more precise than a generic material designation (e.g. “EPDM”).
A typical “line callout” for a EPDM rubber may look something like this:
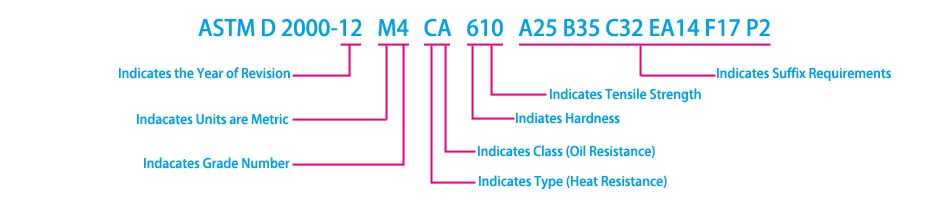
12:
The year of revision:In this case, the year is 2012.
M:
The presence of an ‘M’ indicates metric (SI) units, in particular tensile strength in MPa and temperatures in °C. The absence of an ‘M’ indicates English (imperial) units, in particular tensile strength in psi and temperatures in °F. Metric units are the current standard.
4 – Grade Number:
The Grade Number designates instances where more extensive tests are required.If the grade number is 1, then only the basic requirements of the D2000 specification apply. If the grade number is other than 1, additional requirements apply (e.g. ozone resistance, low temperature resistance, etc.) and are specified by the Suffix Requirements section of the line callout.
C – Type:
Type indicates the heat resistance properties of the elastomer compound.With each type, the elastomer compound must meet the following requirements after 70 hours of heat aging at a specified temperature.
- Change in tensile strength: ±30%
- Change in hardness: -50% max.
- Change in hardness ±15 points
The specified temperatures at which elastomer compound shall be tested for determining type are shown in table 1.

A – Class:
Class indicates the oil resistance properties of the elastomer compound.Oil resistance measures the maximum amount of volume swell by percentage (Table 2) occurring after 70-h immersion in oil at a specific temperature from Table 1.
ASTM D 2000 defines durometer hardness and tensile strength with a three-digit number. In this case, it is 610
6 – Hardness:
6 denotes an elastomer compound with a durometer hardness of 60± 5 A.
10 – Tensile Strength:
This indicates the minimum tensile strength of the elastomer compound. If the designation has an M after the year of revision, then this call-out is stated in Metric units, megapascals (MPa). If no M is present, then the call-out is specifying the English unit, pounds-per-square inch (psi). In this case, the 10 indicates that the tensile strength must be at least 10 MPa. The conversion to psi is:
MPa x 145 = psi.
Therefore, the psi Tensile Strength requirement of this designation is 10 x 145 = 1450psi.
Suffix Requirements:
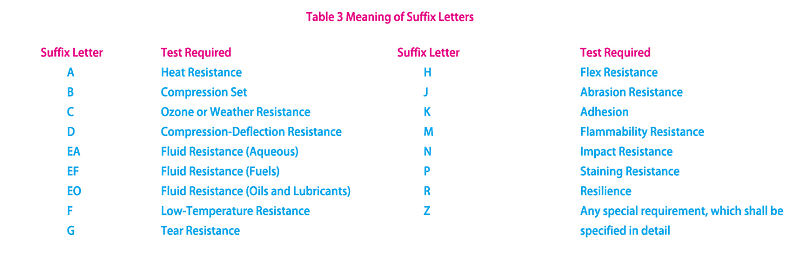
These indicate the additional testing requirements needed to satisfy this specification call-out. Each requirement is comprised of a suffix letter and two suffix numbers. The suffix letters, together with their meanings are shown in Table 3. The first suffix number indicates the test method; time of test is part of the method and is taken from the listings in Table 5 (please refer to Table 5 in ASTM D 2000 standard). The second suffix number, if used, indicates the temperature of test and taken from Table 4 (please refer to Table 4 in ASTM D 2000 standard).
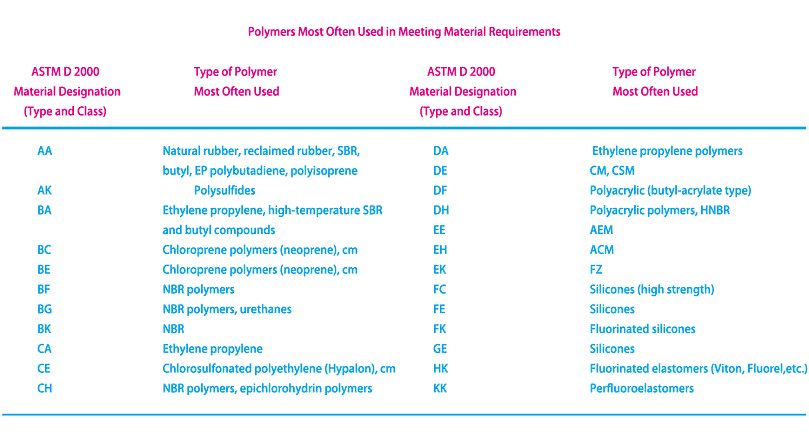
The following table lists the ASTM D 2000 classification system material designations (type and class) and the type of polymer most often used in meeting the material requirements (type and class):
Note: SAE J200 – Classification System for Rubber Materials – is technically equivalent to ASTM D 2000.
